The ideas is that encoders are very powerful at extracting vectors (features) that carry meaningful information of the sequence
- What is an encoder model?
- What does the encoder model do?
- What is “self-attention” and “bi-directional” attention component of an encoder model?
- How does encoder model pre-training work?
- What does the encoder model output?
- Why should we use an encoder? What are they best suited for?
- Real-world examples
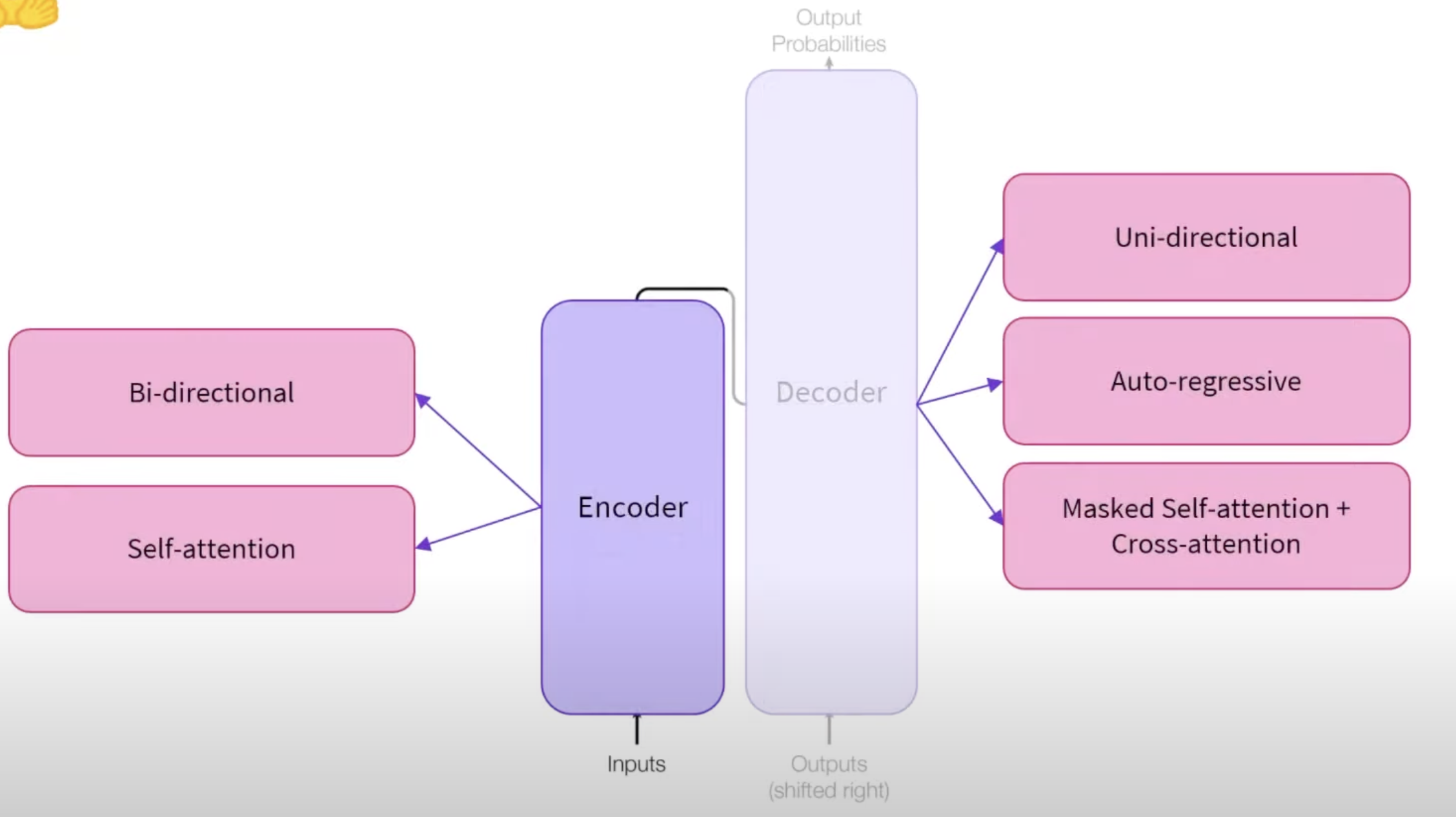
Encoder models use only the encoder of a Transformer model.
What is an encoder model?
It’s a neural network model designed to process/understand input text (sequences) by converting each word into a feature-rich vector representation that captures both the meaning of the word and its context within the sentence. These models are commonly used in NLP (NLP) tasks because they excel at understanding and representing textual data in a way that can be used for
- sentence classification,
- named entity recognition, and
- question answering. Encoder models typically form the first half of the Transformer architecture, designed to “encode” the entire input sequence into contextualised embeddings.
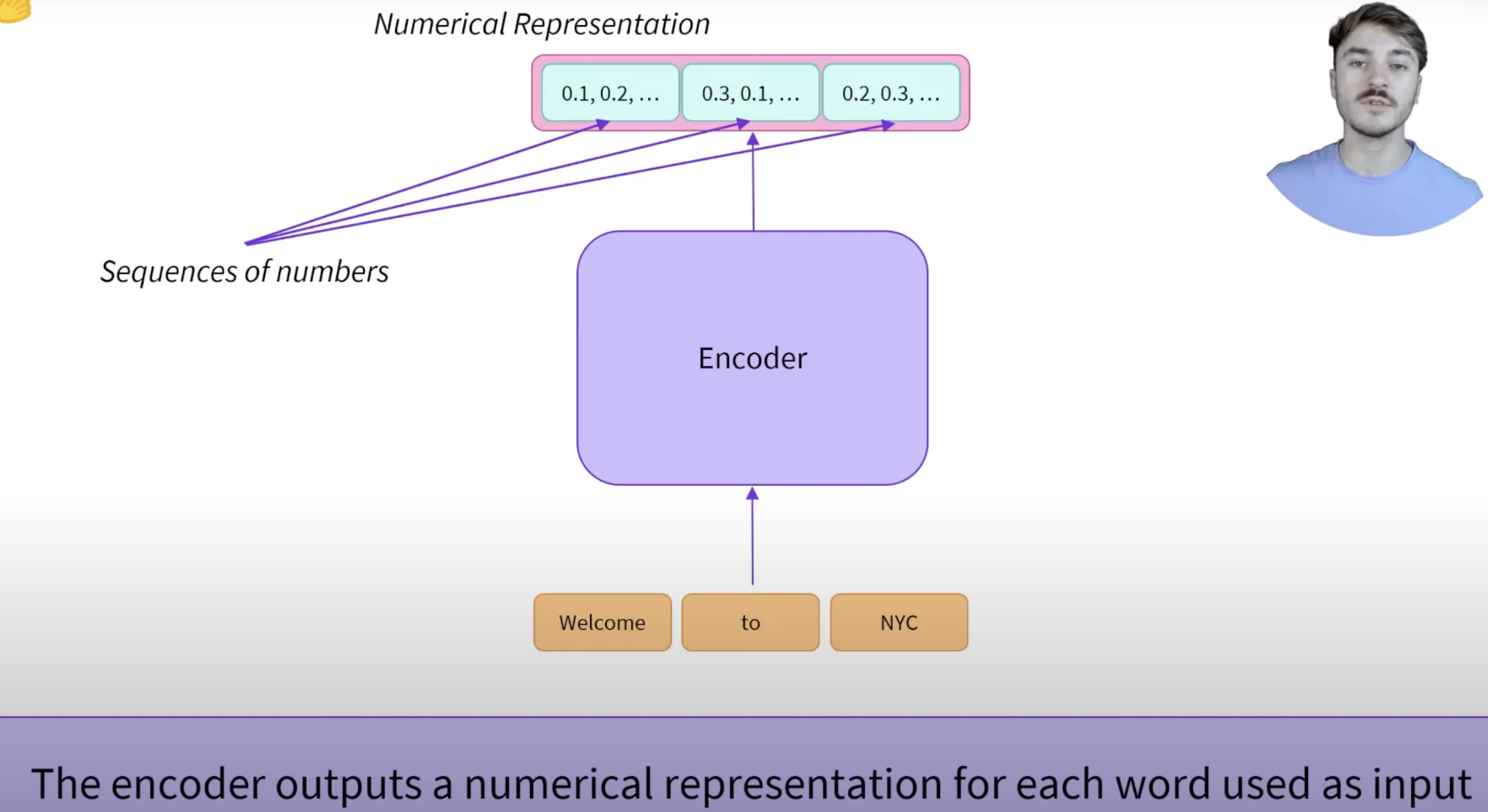
What does the encoder model do?
The encoder model processes input sequences of text, creating a set of context-aware representations (feature vectors) for each word. It does this by analyzing the relationships between words through the self-attention mechanism, effectively capturing the meaning of words based on their surrounding context. These encoded representations can then be used for various downstream tasks, such as classification, prediction, or information retrieval.
What is “self-attention” and “bi-directional” attention component of an encoder model?
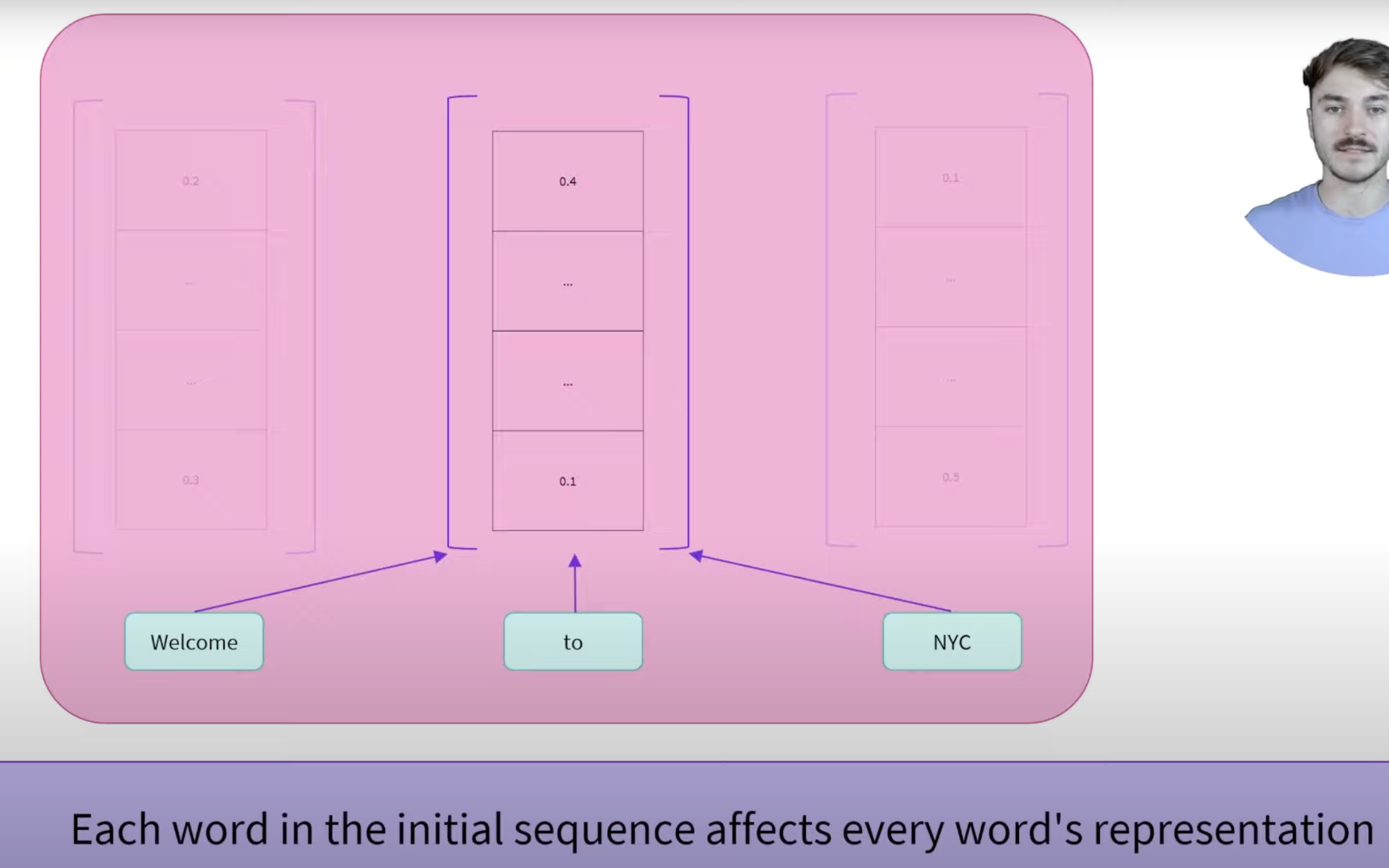
Self-attention is the mechanism that allows each word (or token) in a sequence to attend to, or focus on, every other word, including itself, assigning attention scores based on the relevance between words. This helps capture dependencies and relationships within the sentence, enabling a nuanced understanding of context.
The bi-directional component refers to how encoder models, such as BERT, utilize self-attention to process words in both directions—considering both the left (preceding) and right (succeeding) words for each word in the sentence. This means each word’s context is fully represented, allowing the model to understand the meaning of words that may depend on both past and future information within the sentence.
How does encoder model pre-training work?
The pretraining of these models usually revolves around somehow corrupting a given sentence (for instance, by masking random words in it) and tasking the model with finding or reconstructing the initial sentence.
During pre-training, encoder models learn language patterns through tasks that require understanding context.
- One common approach is the masked language modeling (MLM) task, used in models like BERT. In MLM, the model masks (hides) some words in the sentence and tries to predict them based on the surrounding context. By repeatedly solving this task on a large text corpus, the model learns rich, contextual representations for words.
- Another approach, as used in ELECTRA, involves training the model to detect whether words in a sentence are real or replaced, adding robustness to the model’s understanding of language.
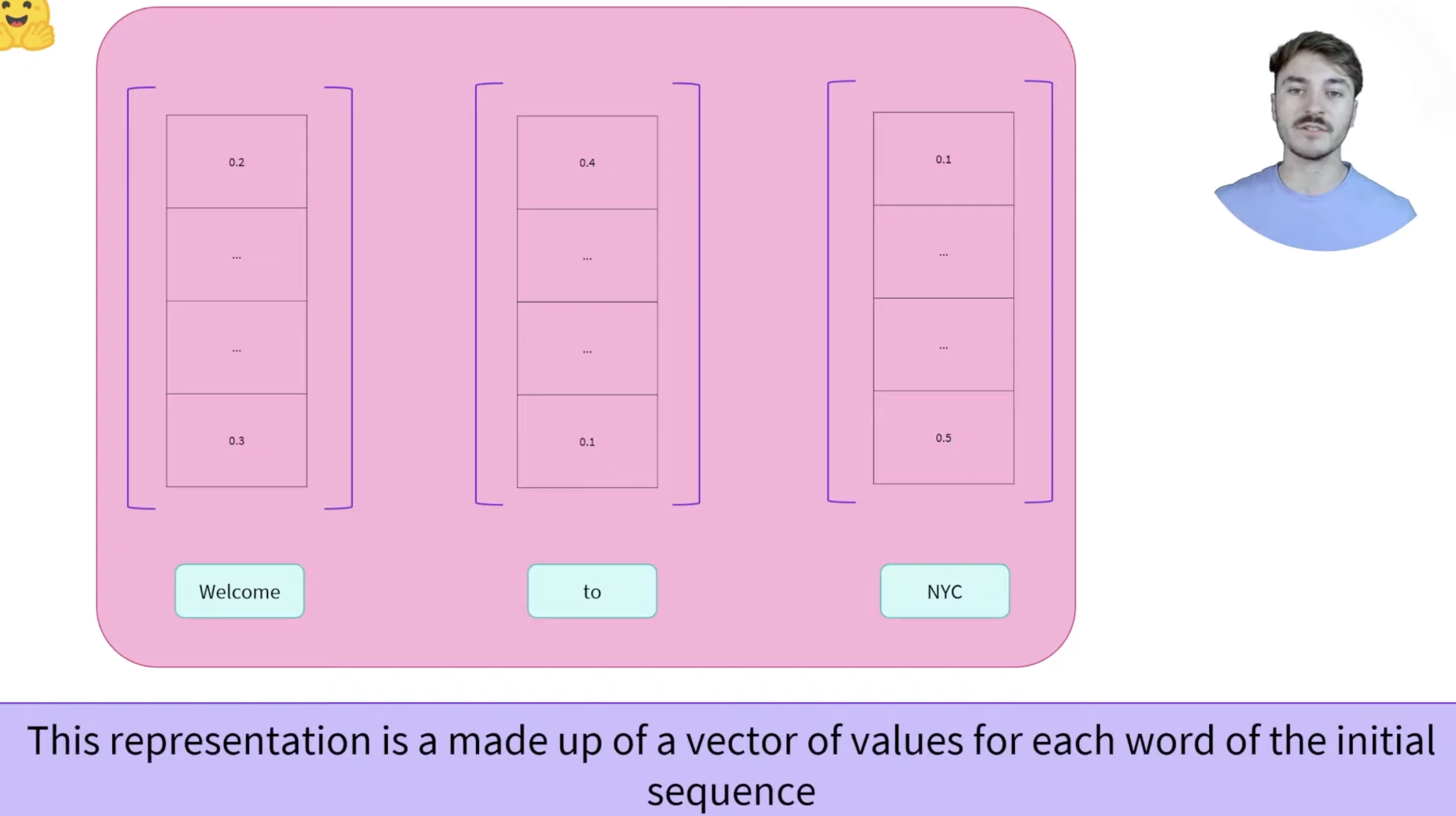
What does the encoder model output?
Encoder models output a feature vector (or embedding) for each word in the input sequence. This feature vector is a high-dimensional numerical representation that encodes the word’s meaning along with its context.
For example, in the base BERT model, each word’s feature vector has 768 dimensions. The values in these vectors represent the model’s learned understanding of each word’s meaning in relation to the other words in the sentence, allowing downstream tasks to utilize this contextualized information for better performance.

Why should we use an encoder? What are they best suited for?

They excel at tasks that require a deep understanding of sentence structure and context. They are particularly effective in:
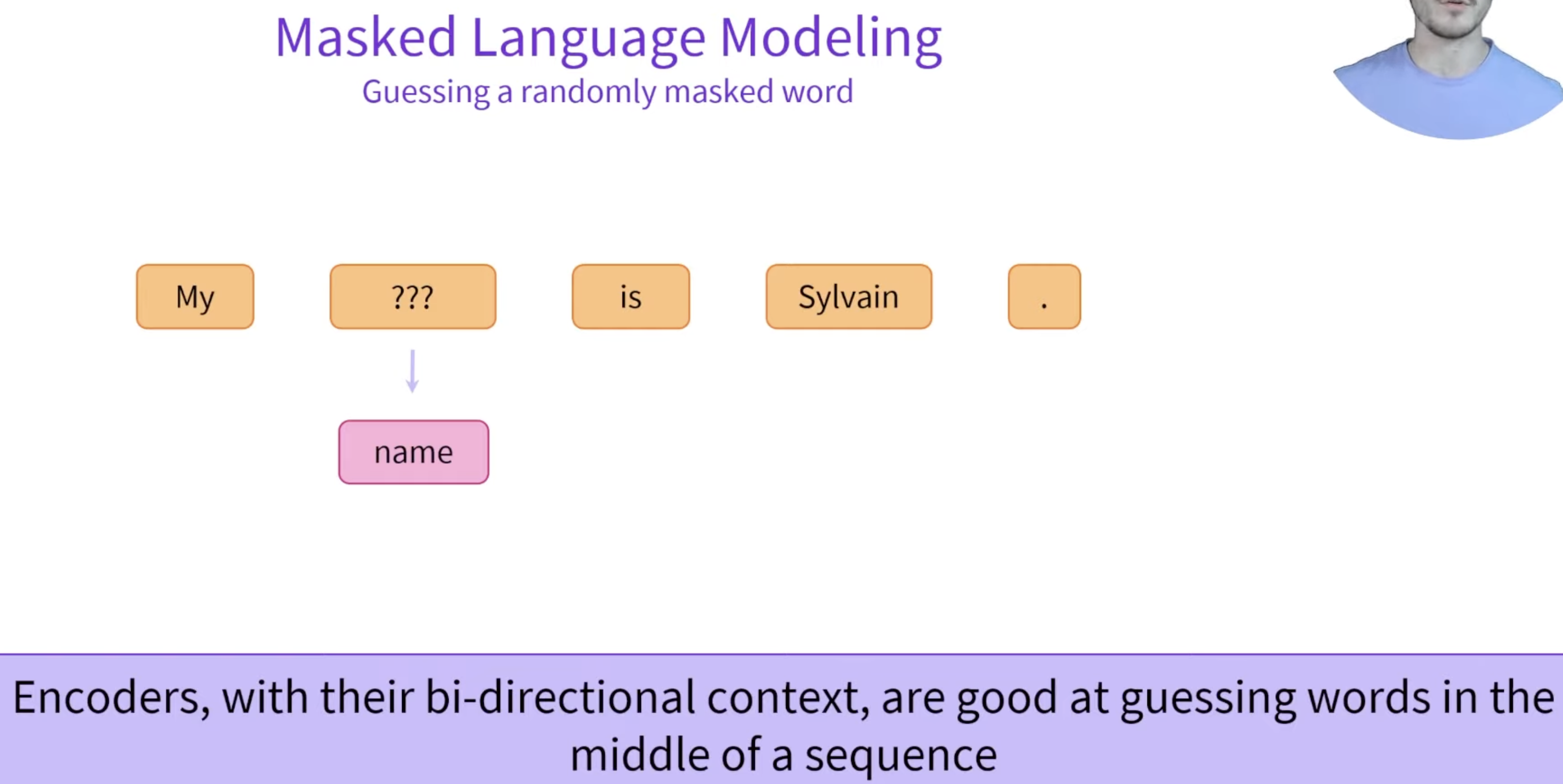
Example - MLM - Predicting the missing word
Encoders (MLM), with bi-directional context, are good at guessing words in the middle of a sequence. This requires both semantic and syntacting understanding.
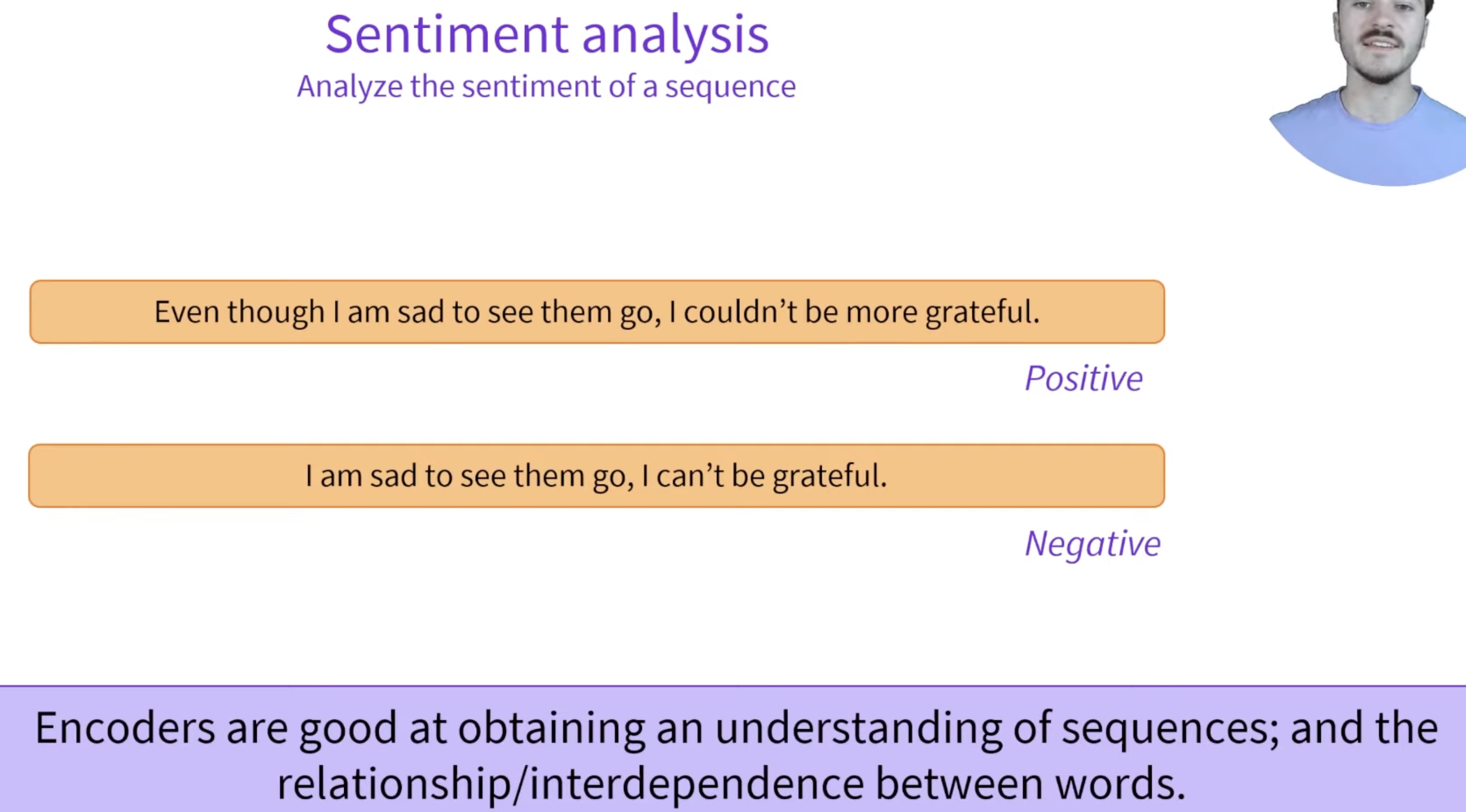
Example - Sentiment analysis
Sentence Classification (e.g., sentiment analysis) where the entire sentence’s meaning is needed.
Example - NER
Identifying specific entities within a sentence, such as names of people, locations, and organizations. For more details, refer NER
Example - Extractive Question Answering
The model must locate the relevant parts of a text to answer specific questions by identifying spans in the text, often by looking at context across the sentence.
Real-world examples
- Customer Support Chatbots: Encoder models are widely used in chatbots to accurately interpret user questions and requests. For instance, a chatbot may use an encoder model to classify whether a user inquiry is about billing, technical support, or general questions, and then provide contextually relevant responses.
- Legal Document Analysis: In legal tech, encoder models help identify and extract named entities, such as names of parties, case references, or legal terms, from contracts and other documents. This enables automatic document tagging, faster information retrieval, and helps legal professionals in conducting more efficient document reviews.