Speaker: Eileen Poon, Nutritionist | LinkedIN
TL;DR Eat Right for a Healthy Immune System
- REDUCE inflammatory food
- INCREASE whole, nutrient-dense food
- INCLUDE phytochemicals
- INCLUDE prebiotics & probiotics-rich foods
1. Factors affecting the Immune System
Immune System
- Protect ourselves (e.g., Fever)
- Body’s natural fever response helps fight viruses by raising temperature to kill pathogens, though many people counteract this by taking fever-reducing medication too quickly.
- Acts as a barrier (e.g., Nose hairs)
- When we are sleeping, immunity is lowest.
- All the dust particles and dust mites goes through nose
- When we wake up, the body will try to remove those foreign bodies.
- It removes through the same way it entered (through mucous which we call as a Sinus)
- When we are sleeping, immunity is lowest.
Signs of Weak Immune System
- Get sick more frequently
- Longer recovery
- Tummy troubles
- Wounds are slow to heal
- Feel tired all the time
- Other signs
- Having more than four ear infections in one year
- Developing pneumonia twice during one-year period
- Suffering from chronic sinusitis or more than three episodes of bacterial sinusitis in a year
- Needing more than two courses of antibiotics a year
Factors that Influence Our Immune System
- Ageing
- Environmental Toxins: Sinus in the morning due to dust in the air
- Excess Weight: Fat tissues promote inflammation in the body
- Chronic Mental Stress: Release hormones that suppress inflammation
- Lack of Sleep
- Poor Diet (or) Nutrition Imbalance.
How Food Affect Our Immune System?
- ~70% of immune system found in your gut
- A significant part of your immune system interacts with what you eat
- Two type of soldiers in the intestine/gut
- Good Army: Their food is fiber food, vegetables, which contain prebiotics.
- Bad Army
Right Nutrition = Strong Immunity
- Avoid malnutrition or micronutrient deficiencies
- Feed your immune system with right nutrients to function optimally
2. Do ‘Immunity-Boosting’ Supplement works?
- It’s still the best to get nutrients from food whenever possible.
- Over supplementing can be harmful to your body.
- Immunity-boosting supplements can be marketing tactic
- Limited evidence to support the idea that specific supplements can “boost” immunity in a way that prevents illness.
3. Eat Right for a Healthy Immune System
1. REDUCE inflammatory food
- Ultra-processed foods such as chicken hotdog, nuggets, etc.
- Sugary food and beverages that significantly impact blood sugar levels
- Strategy
- Remove
- Reduce
- Replace
2.. INCREASE Whole, Nutrient-dense food
- Protein: Building of antibodies and immune system cells.
- Vitamin D: Important for immune regulation & active immune cells
- Mushroom - Contain Vitamin D and contain special prebiotics which feed our gut bacteria
- Iron: Needed to make immune cells & red blood cells
- Zinc: Wound healing
- Fibre: Reduce and Inflammation
- Vitamin A: Regulate immune system, protect against infection by keeping your skin tissue healthy
- Vitamin E: Acts as antioxidant, protecting cell membranes from damage
- Vitamin C: Antioxidant that protects cells from damage caused by free radicals. Vital to
- barrier function & wound healing via collagen promotion
- recruit cells to targets
- function of white blood cells
- antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity
- reduce the duration and severity of the common cold a bit
- maintain higher blood levels if you supplement it multiple times per day instead of just once
Fruits & Vegetables: Full of vitamins & minerals
2 servings of fruits & 2 servings of vegetables per day
3. INCLUDE Phytochemicals
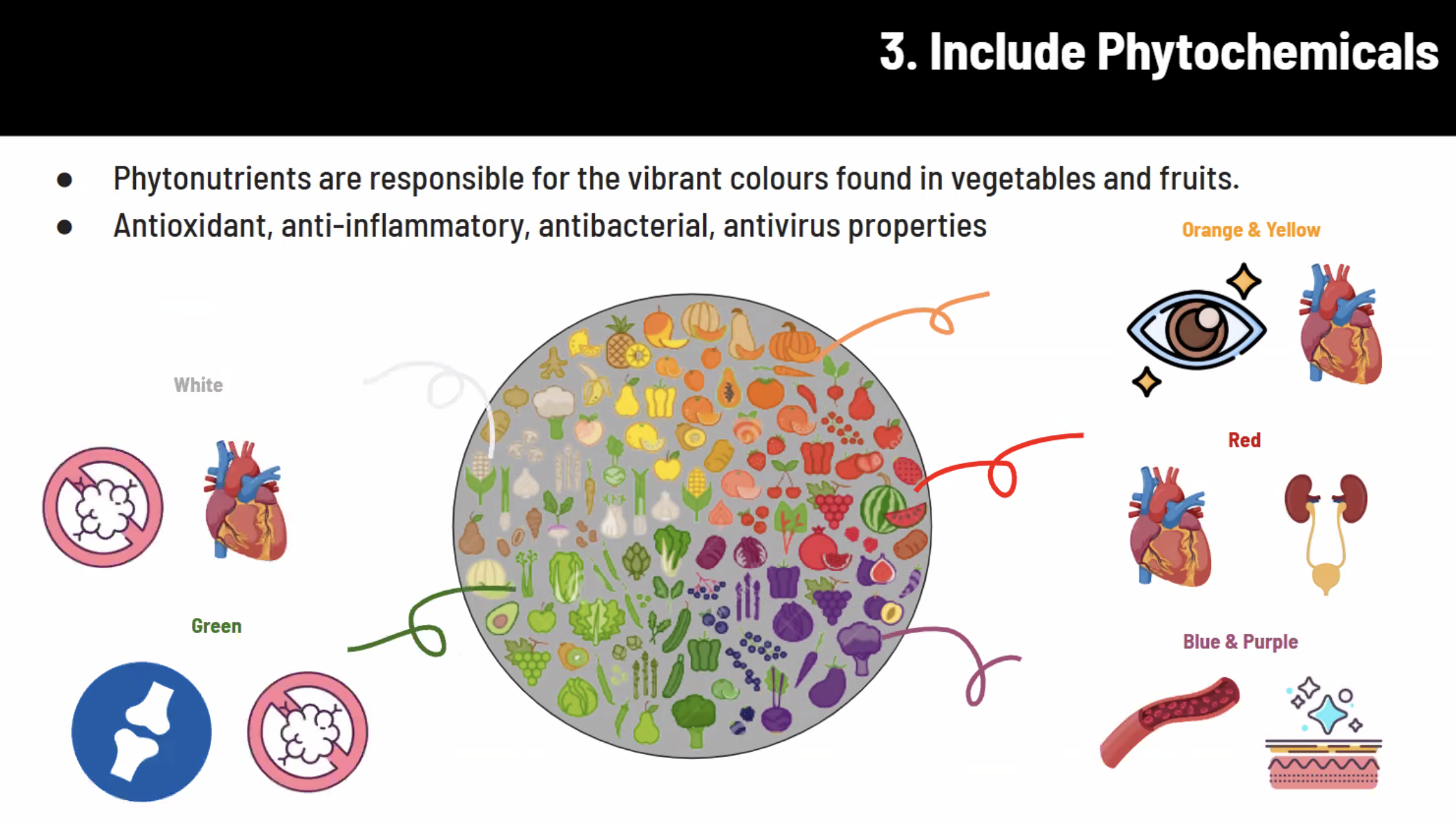
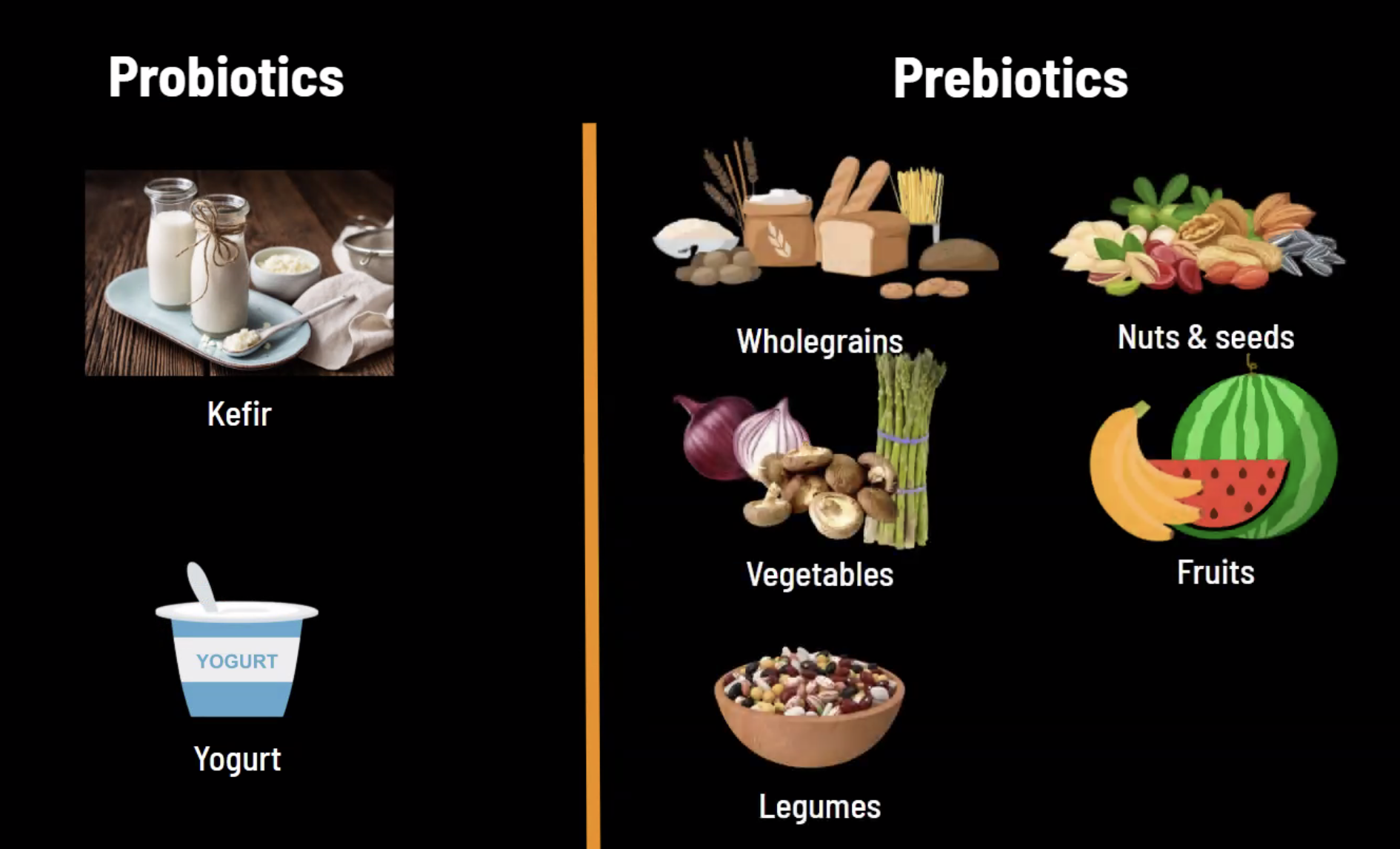
4. INCLUDE Prebiotics & Probiotics-rich foods
- Probiotics: Live microorganisms that are intended to have health benefits when consumed or applied to the body.
- Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium
- Prebiotics: Foods we eat and are thought to feed the “good” bacteria in our gut.
AI Summary
Eileen, a diet and nutrition therapist, leads a session on immune system health, explaining that the body’s natural fever response helps fight viruses by raising temperature to kill pathogens, though many people counteract this by taking fever-reducing medication too quickly. She discusses how the immune system works as a complex defense mechanism, including how nasal hairs act as barriers and how sinus issues often occur at night when immunity is lowest, emphasizing that medication can weaken the immune system while natural remedies like vitamin C can help strengthen it. She concludes by explaining that frequent infections (2-3 times per year) can be an indicator of a weakened immune system.
Based on the webinar discussion, these main topics have been covered:
-
Factors affecting the immune system
-
Discussion on immunity boosting supplements and their effectiveness
-
Guidelines for eating right for a healthy immune system
-
Immune system functionality:
-
Body’s fever response mechanism
-
Role of physical barriers (lungs, nose hair)
-
Sinus conditions and immunity
-
-
Symptoms of weak immune system:
- Frequent infections
- Longer recovery time from illnesses
In this wellbeing webinar, Eileen, a diet and nutrition therapist, covered key aspects of immunity and nutrition:
-
Immune System Function
- Natural fever response helps fight viruses
- Physical barriers like nose hair protect against pathogens
- 70% of immune system located in digestive tract
-
Weak Immunity Signs
- Frequent infections (2-3 times yearly)
- Slow wound healing
- Persistent fatigue
- Chronic sinus issues
-
Nutrition Guidelines
- Balanced protein intake (1.5g per kg body weight)
- Diverse colored fruits and vegetables for phytonutrients
- Prebiotic foods for gut health
- Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and kefir
-
Dietary Recommendations
- Reduce ultra-processed foods
- Limit sugar intake
- Include vitamin-rich foods (C, D, E)
- Focus on whole foods
- Add mushrooms for vitamin D
- Include garlic for anti-inflammatory benefits